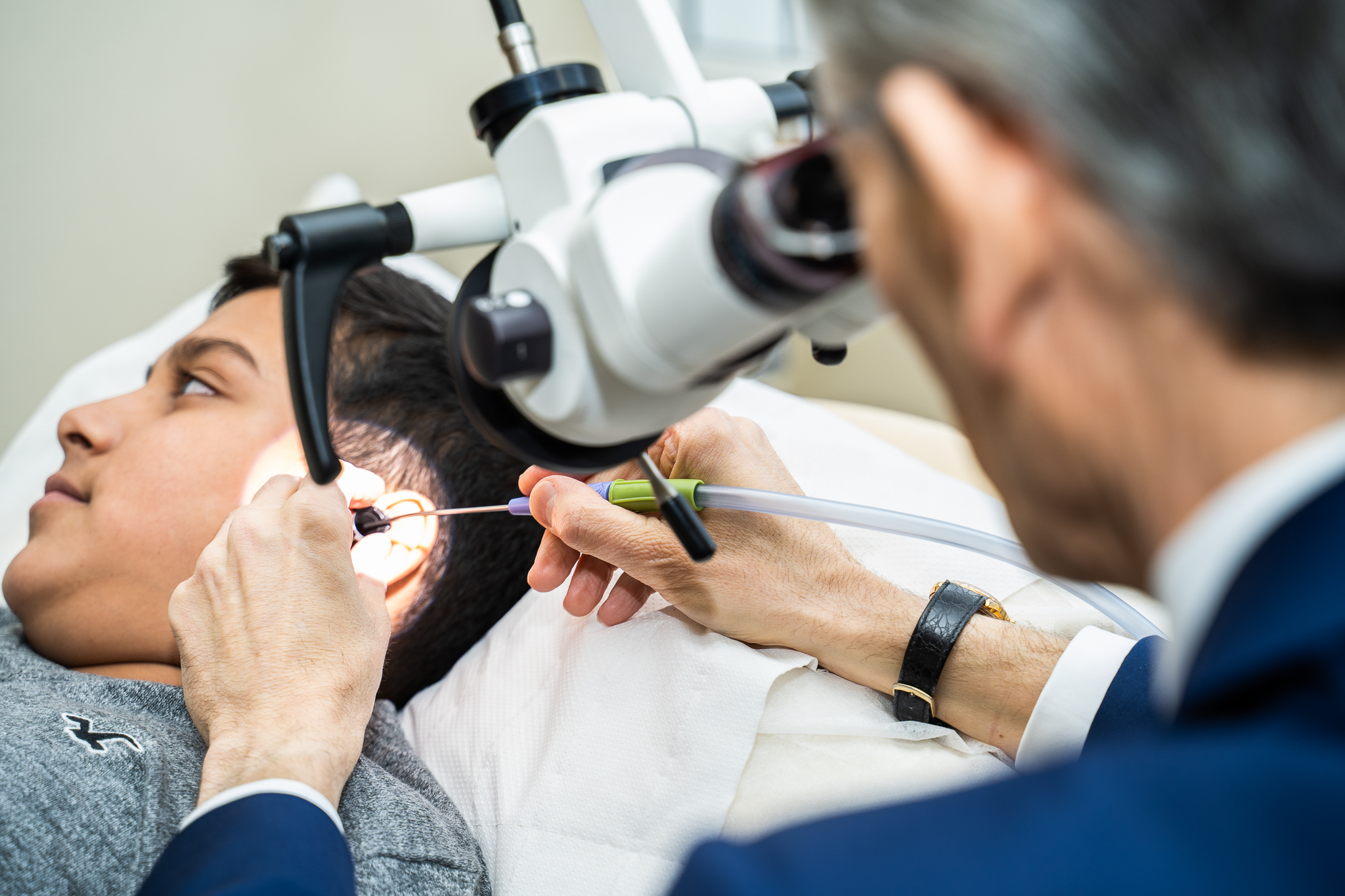
Balloon Eustachian Tube Dilatation
Balloon Eustachian tube dilatation (BETD) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD), a condition characterized by impaired pressure equalization and ventilation of the middle ear. While BETD is generally considered safe and effective, there may be instances where medico-legal concerns arise. This article provides an overview of BETD, discusses its indications, potential complications, and addresses the medico-legal aspects that may be relevant in cases involving this procedure.
Indications for BETD: BETD is typically considered as a treatment option for individuals with chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction who have not responded to conservative management. Common indications for BETD include:
- Persistent Eustachian tube dysfunction: When traditional treatments such as nasal steroid sprays, decongestants, or autoinsufflation techniques fail to provide relief, BETD may be considered.
- Recurrent middle ear infections: Eustachian tube dysfunction can lead to the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear, resulting in recurrent otitis media. BETD may be recommended to improve middle ear ventilation and reduce the frequency of infections.
- Barotrauma: Individuals who frequently experience discomfort or pain during changes in altitude or pressure, such as during air travel or scuba diving, may benefit from BETD to enhance Eustachian tube function.
Potential Complications: While BETD is generally considered safe, it is important to be aware of potential complications. These may include:
- Pain or discomfort: Patients may experience temporary discomfort or pain during or after the procedure, which is typically managed with pain medication.
- Infection: Any invasive procedure carries a risk of infection. Strict adherence to aseptic techniques is essential to minimize this risk.
- Bleeding: Although uncommon, there is a slight risk of bleeding during or after the procedure. Proper technique and monitoring can help mitigate this risk.
- Perforation: In rare cases, the balloon dilatation may cause a perforation of the Eustachian tube or the tympanic membrane. This can lead to in rare cases, surgical emphysema of the face and neck.
Medico-Legal Considerations: In cases involving BETD, several medico-legal considerations should be taken into account:
- Informed consent: Obtaining informed consent from the patient or their legal guardian is crucial. The patient must be provided with comprehensive information about the procedure, including its purpose, potential risks, benefits, alternatives, and potential complications. Documentation of the informed consent process is essential for medico-legal purposes.
- Documentation: Thorough and accurate documentation is vital. Detailed notes regarding the patient’s medical history, diagnostic evaluations, treatment plan, procedure details, any complications encountered, and post-procedure follow-up should be recorded meticulously.
- Standard of care: Healthcare professionals performing BETD are expected to adhere to the standard of care, which is the level of skill and knowledge commonly possessed and exercised by practitioners in the same field. Deviation from the standard of care may lead to allegations of medical negligence.
- Adverse outcomes: If complications arise during or after BETD, it is essential to promptly address them and provide appropriate management. Documenting adverse outcomes, steps taken to address them, and communication with the patient or their family is crucial in medico-legal cases.
Conclusion: Balloon Eustachian tube dilatation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat Eustachian tube dysfunction. While generally safe and effective, medico-legal considerations must be taken into account. By considering the indications, potential complications, and medico-legal aspects discussed in this article, healthcare professionals can ensure safe and appropriate care while protecting themselves in cases involving BETD-related medico-legal concerns.